e-commerce shipping solutions
Eco-friendly packaging solutions
International shipping guidelines
advanced distribution, distribution, distribution solutions, distribution strategies, fulfillment, fulfillment solutions, fulfillment strategies, logistics, logistics management, shipping, shipping logistics, strategic fulfillment, supply chain, supply chain drivers, supply chain efficiency, supply chain excellence, supply chain management, supply chain optimization, supply chain performance, supply chain success
prraelogistics
0 Comments
Distribution and Fulfillment: Key Components for a Successful Supply Chain
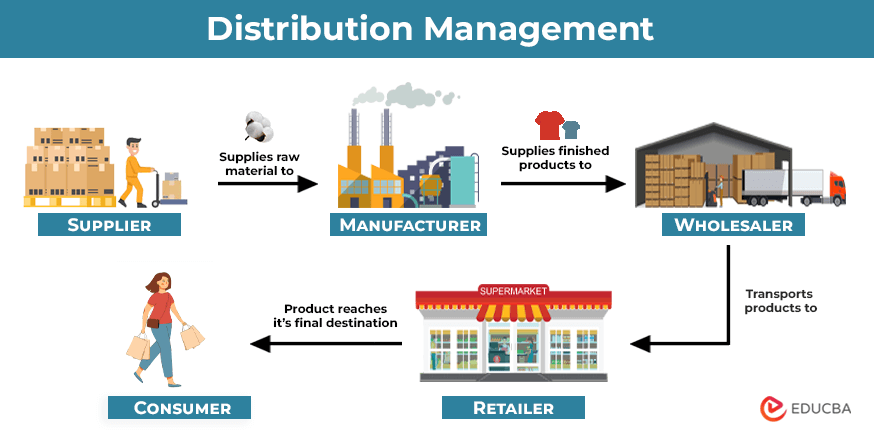
In today’s fast-paced and highly competitive market, businesses must deliver products to their customers quickly, efficiently, and accurately. The processes that ensure this are distribution and fulfillment, which play pivotal roles in the supply chain. These components enable companies to move products from manufacturers or warehouses to the end consumers or retailers. Whether you’re running an e-commerce business or managing a global supply chain, optimizing your distribution and fulfillment processes is essential for customer satisfaction and long-term success.
In this blog post, we will dive into the key aspects of distribution and fulfillment, their importance in modern supply chains, best practices to enhance efficiency, and emerging trends shaping the future of these operations.

What is Distribution?
Distribution refers to the process of storing, transporting, and delivering goods to their intended destinations, whether that be a warehouse, retail store, or customer. It’s the middle stage of the supply chain that bridges the gap between manufacturers or suppliers and the market. Efficient distribution ensures that products arrive at the right place, at the right time, and in good condition.
Key Functions of Distribution
- Warehousing: Storage of products in a centralized or decentralized facility until they are ready to be shipped to their next destination. Warehouses play a crucial role in ensuring inventory is managed effectively, organized, and ready for fulfillment.
- Inventory Management: Ensuring that the right amount of stock is available to meet demand without overstocking. Effective inventory management helps prevent shortages and reduce holding costs.
- Order Processing: The process of receiving and handling customer orders. This includes picking, packing, and preparing the goods for shipping. Order accuracy and speed are critical factors in customer satisfaction.
- Transportation: Moving products from one location to another using various modes of transport, such as road, rail, air, or sea. Efficient transportation helps reduce lead times and shipping costs.
- Logistics Coordination: Synchronizing the movement of goods between different locations and managing multiple transportation providers to optimize delivery routes and schedules.
What is Fulfillment?
Fulfillment refers to the end-to-end process of receiving, processing, and delivering orders to customers. It encompasses everything from warehousing and inventory management to packing and shipping orders. Fulfillment operations are critical to e-commerce businesses and retailers who want to ensure that products reach customers quickly and accurately.
Key Steps in Fulfillment
Returns Processing: If a customer returns a product, the fulfillment team is responsible for processing the return, ensuring it is restocked (if possible), and managing refunds or exchanges.
The Importance of Distribution and Fulfillment in the Supply Chain
Both distribution and fulfillment are vital to ensuring the smooth operation of a supply chain. They impact key performance indicators such as order accuracy, delivery times, customer satisfaction, and overall operational efficiency.
1. Customer Satisfaction
Efficient distribution and fulfillment ensure that customers receive their products quickly and in perfect condition. Delays, errors, or damage during the fulfillment process can lead to negative customer experiences, damaging brand reputation.
2. Cost Efficiency
Optimizing distribution and fulfillment processes helps reduce operational costs by minimizing transportation expenses, reducing storage fees, and improving order accuracy. Businesses that streamline these processes can pass the savings on to customers or reinvest them in other areas of the company.
3. Inventory Management
Proper distribution and fulfillment help businesses maintain accurate inventory levels, preventing overstocking or stockouts. This ensures that businesses can meet customer demand without holding excess inventory, which can tie up valuable resources.
4. Speed to Market
The faster a product moves through the distribution and fulfillment process, the sooner it reaches the customer. In competitive industries, speed is a major differentiator, especially for e-commerce and retail companies offering same-day or next-day delivery.
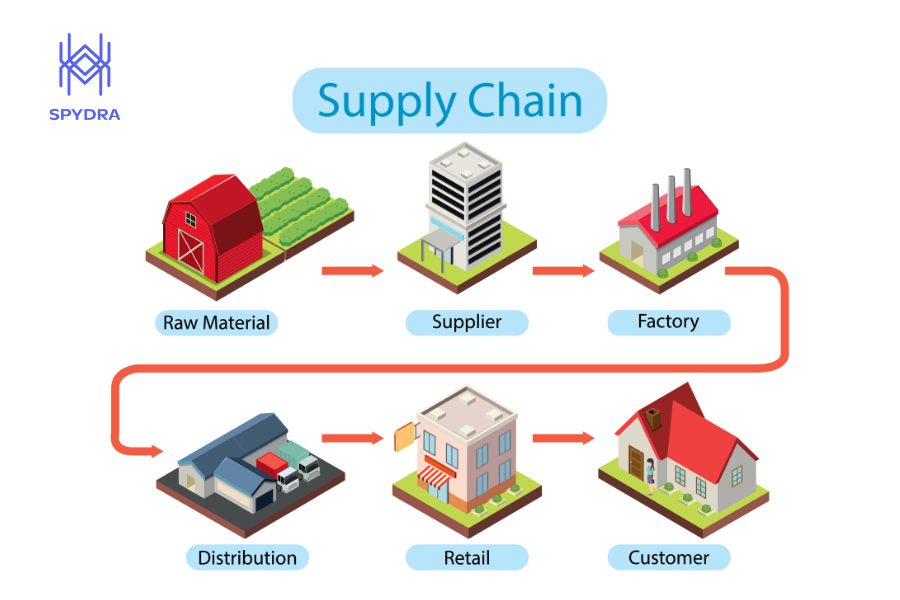
Best Practices for Optimizing Distribution and Fulfillment
To enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction, businesses must adopt best practices that optimize their distribution and fulfillment operations. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Automate Where Possible
Automation is a game-changer in both distribution and fulfillment. Automated systems, such as robotic pickers, conveyor belts, and warehouse management software (WMS), can significantly reduce human error, improve picking and packing speeds, and increase overall throughput. For example, Amazon’s use of robotics in its fulfillment centers has greatly enhanced order processing and fulfillment efficiency.
2. Leverage Data Analytics
Data analytics can provide valuable insights into distribution and fulfillment performance, helping businesses identify bottlenecks, optimize shipping routes, and forecast inventory needs. By analyzing historical data and real-time metrics, companies can make informed decisions that reduce costs and improve service levels.
3. Optimize Inventory Placement
Proper inventory placement within distribution centers and warehouses is key to reducing picking times and improving overall efficiency. Grouping popular products near the packing area, implementing slotting strategies, and minimizing walking distances can significantly improve fulfillment speed.
4. Offer Multiple Shipping Options
In today’s world, customers expect flexibility in shipping options. Offering a range of delivery speeds (standard, express, same-day) gives customers the freedom to choose based on their needs and preferences. This also enables businesses to better manage shipping costs by balancing fast and cost-effective options.
5. Partner with Third-Party Logistics Providers (3PLs)
Outsourcing distribution and fulfillment to a 3PL can help businesses scale their operations without the overhead of maintaining their own warehouses, technology, or transportation fleet. 3PLs offer expertise in logistics, technology, and fulfillment that can optimize the process, allowing businesses to focus on growth.
6. Use Cloud-Based Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Cloud-based WMS solutions allow for real-time inventory tracking, order processing, and data sharing across multiple locations. This is particularly valuable for businesses with complex distribution networks or those expanding into new regions. Cloud WMS also provides the flexibility to scale operations as the business grows.
7. Efficient Returns Management
A seamless returns process is critical to customer retention and satisfaction, especially in e-commerce. Businesses should ensure that returned items are processed quickly and restocked or disposed of in a timely manner. A well-handled returns process can increase customer trust and encourage repeat business.
Tag
advanced distribution distribution distribution solutions distribution strategies fulfillment fulfillment solutions fulfillment strategies logistics logistics management shipping shipping logistics strategic fulfillment supply chain supply chain drivers supply chain efficiency supply chain excellence supply chain management supply chain optimization supply chain performance supply chain success







Post Comment